Results
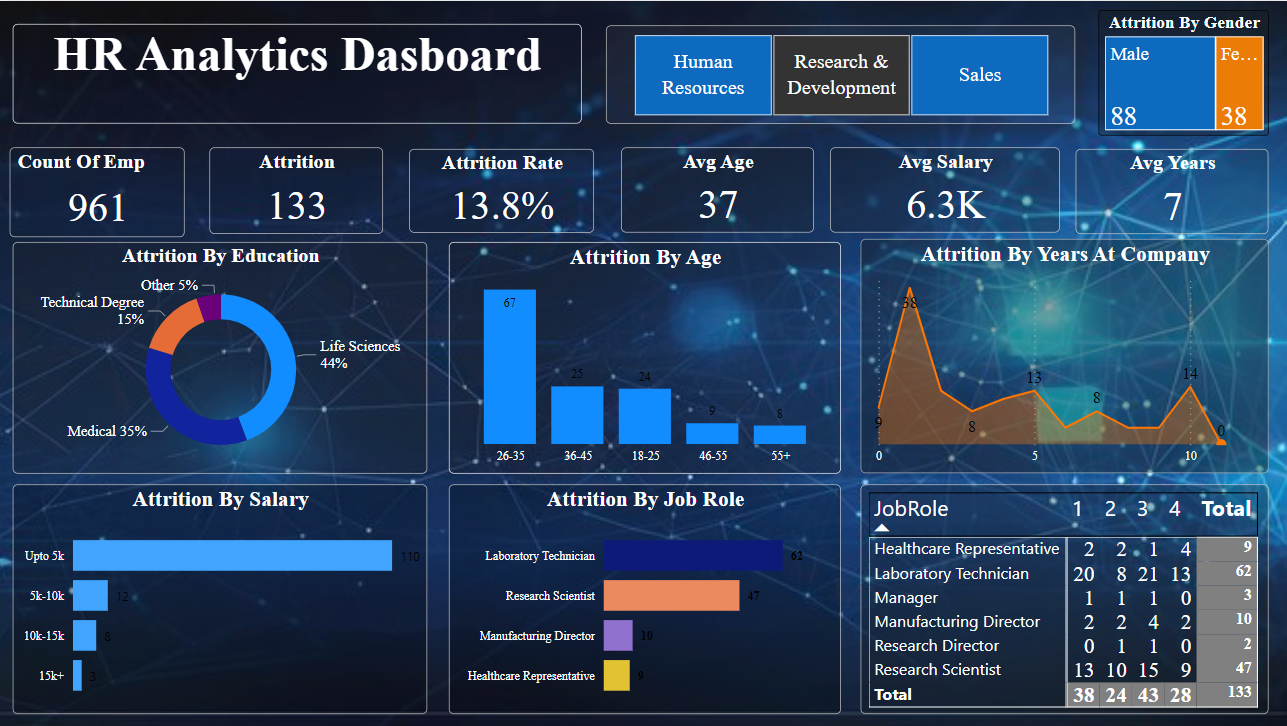
1. Key Metrics
- Total Number of Employees: 1,413
- Attrition Count: 239
- Attrition Rate: 16.1%
- Average Age of Employees: 37 years
- Average Salary: $6.5K
- Average Tenure: 7 years
2. Attrition by Education
Interpretation: Employees with Life Sciences and Medical degrees are leaving the company at higher rates. This could indicate that the company may not be meeting the career expectations or job satisfaction needs of these highly educated employees.
Improvement: Consider conducting exit interviews or surveys with employees in these educational categories to understand the specific reasons for attrition. Based on feedback, the company could tailor retention strategies, such as offering more career development opportunities or competitive benefits packages.
3. Attrition by Age
Interpretation: Younger employees, particularly those aged 26-35, are the most likely to leave the company. This could suggest that younger workers are not finding the growth opportunities they seek, or they might be exploring other job markets for better offers.
Improvement: To retain younger employees, the company could focus on providing clearer career progression paths, mentorship programs, and opportunities for continuous learning and development. Additionally, offering flexible work arrangements might appeal to this age group.
4. Attrition by Job Role
Interpretation: Laboratory Technicians and Research Scientists are experiencing high levels of attrition. This could be due to job dissatisfaction, lack of advancement opportunities, or competitive offers from other companies.
Improvement: Investigate the specific challenges faced by employees in these roles. Consider improving working conditions, enhancing job roles, offering better compensation, or providing clear paths for advancement. Strengthening the organizational culture within these roles might also reduce turnover.
5. Attrition by Salary
Interpretation: The majority of attrition is occurring among employees earning up to 5K. This suggests that lower-paid employees may be leaving due to financial dissatisfaction or the allure of better-paying jobs elsewhere.
Improvement: Reevaluate the company’s compensation structure, particularly for lower-paid employees. Offering competitive salaries, performance-based incentives, and additional benefits could help retain talent. Also, consider creating pathways for upward mobility for these employees.
6. Attrition by Years at Company
Interpretation: There’s a significant spike in attrition around the 2-year mark, which might indicate that employees are leaving before they fully settle into their roles, possibly due to unmet expectations or insufficient engagement.
Improvement: Implement stronger onboarding programs and ensure that new employees have clear expectations and a support system in place. Regular check-ins during the first few years, career development discussions, and employee engagement activities could help retain employees beyond this critical period.

 Excel
Excel
 Power BI
Power BI